如何实现工具使用
选择模型
我们推荐使用最新的 Claude Opus (4.6) 模型来处理复杂工具和模糊查询;它能更好地处理多个工具,并在需要时寻求澄清。
对于简单的工具,可以使用 Claude Haiku 模型,但请注意它可能会推断缺失的参数。
如果将 Claude 与工具使用和扩展思考一起使用,请参阅我们的指南此处了解更多信息。
指定客户端工具
客户端工具(包括 Anthropic 定义的和用户定义的)在 API 请求的 tools 顶级参数中指定。每个工具定义包括:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
name | 工具的名称。必须匹配正则表达式 ^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{1,64}$。 |
description | 工具功能、使用时机和行为方式的详细纯文本描述。 |
input_schema | 一个 JSON Schema 对象,定义工具的预期参数。 |
input_examples | (可选,beta)一个示例输入对象数组,帮助 Claude 理解如何使用该工具。参见提供工具使用示例。 |
工具使用系统提示
当你使用 tools 参数调用 Claude API 时,我们会根据工具定义、工具配置和任何用户指定的系统提示构建一个特殊的系统提示。构建的提示旨在指导模型使用指定的工具,并为工具的正常运行提供必要的上下文:
In this environment you have access to a set of tools you can use to answer the user's question.
{{ FORMATTING INSTRUCTIONS }}
String and scalar parameters should be specified as is, while lists and objects should use JSON format. Note that spaces for string values are not stripped. The output is not expected to be valid XML and is parsed with regular expressions.
Here are the functions available in JSONSchema format:
{{ TOOL DEFINITIONS IN JSON SCHEMA }}
{{ USER SYSTEM PROMPT }}
{{ TOOL CONFIGURATION }}工具定义的最佳实践
要在使用工具时获得 Claude 的最佳性能,请遵循以下指南:
- 提供极其详细的描述。 这是影响工具性能的最重要因素。你的描述应该解释关于工具的每个细节,包括:
- 工具的功能
- 何时应该使用(以及何时不应该使用)
- 每个参数的含义及其如何影响工具的行为
- 任何重要的注意事项或限制,例如如果工具名称不明确时工具不返回哪些信息。你能给 Claude 提供的关于工具的上下文越多,它在决定何时以及如何使用工具方面就越出色。每个工具描述至少应有 3-4 句话,如果工具复杂则需要更多。
- 优先考虑描述,但对于复杂工具可以考虑使用
input_examples。 清晰的描述最为重要,但对于具有复杂输入、嵌套对象或格式敏感参数的工具,你可以使用input_examples字段(beta)提供经过模式验证的示例。详见提供工具使用示例。
良好的描述清楚地解释了工具的功能、何时使用、返回什么数据以及 ticker 参数的含义。不良的描述过于简短,让 Claude 对工具的行为和用法留下许多疑问。
提供工具使用示例
你可以提供有效工具输入的具体示例,帮助 Claude 更有效地理解如何使用你的工具。这对于具有嵌套对象、可选参数或格式敏感输入的复杂工具特别有用。
工具使用示例是一个 beta 功能。请为你的提供商包含适当的 beta 头:
| 提供商 | Beta 头 | 支持的模型 |
|---|---|---|
| Claude API, Microsoft Foundry | advanced-tool-use-2025-11-20 | 所有模型 |
| Vertex AI, Amazon Bedrock | tool-examples-2025-10-29 | Claude Opus 4.6, Claude Opus 4.5 |
基本用法
在你的工具定义中添加一个可选的 input_examples 字段,包含一个示例输入对象数组。每个示例必须根据工具的 input_schema 有效:
import anthropic
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-opus-4-6",
max_tokens=1024,
betas=["advanced-tool-use-2025-11-20"],
tools=[
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "The unit of temperature"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
},
"input_examples": [
{
"location": "San Francisco, CA",
"unit": "fahrenheit"
},
{
"location": "Tokyo, Japan",
"unit": "celsius"
},
{
"location": "New York, NY" # 'unit' is optional
}
]
}
],
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in San Francisco?"}
]
)示例与你的工具模式一起包含在提示中,向 Claude 展示格式良好的工具调用的具体模式。这有助于 Claude 理解何时包含可选参数、使用什么格式以及如何构建复杂输入。
要求和限制
- 模式验证 - 每个示例必须根据工具的
input_schema有效。无效的示例会返回 400 错误 - 不支持服务器端工具 - 只有用户定义的工具可以有输入示例
- Token 成本 - 示例会增加提示 token:简单示例约 20-50 个 token,复杂嵌套对象约 100-200 个 token
工具运行器(beta)
工具运行器提供了一个开箱即用的解决方案,用于使用 Claude 执行工具。无需手动处理工具调用、工具结果和对话管理,工具运行器会自动:
- 当 Claude 调用工具时执行工具
- 处理请求/响应循环
- 管理对话状态
- 提供类型安全和验证
我们建议你在大多数工具使用实现中使用工具运行器。
工具运行器目前处于 beta 阶段,可在 Python、TypeScript 和 Ruby SDK 中使用。
通过压缩实现自动上下文管理
工具运行器支持自动压缩,当 token 使用量超过阈值时生成摘要。这允许长时间运行的智能体任务超越上下文窗口限制继续执行。
基本用法
使用 SDK 辅助工具定义工具,然后使用工具运行器执行它们。
工具函数必须返回内容块或内容块数组,包括文本、图像或文档块。这允许工具返回丰富的多模态响应。返回的字符串将被转换为文本内容块。如果你想向 Claude 返回结构化的 JSON 对象,请在返回之前将其编码为 JSON 字符串。数字、布尔值或其他非字符串原始类型也必须转换为字符串。
迭代工具运行器
工具运行器是一个可迭代对象,产生来自 Claude 的消息。这通常被称为"工具调用循环"。每次迭代时,运行器检查 Claude 是否请求了工具使用。如果是,它会调用工具并自动将结果发送回 Claude,然后产生 Claude 的下一条消息以继续你的循环。
你可以在任何迭代中使用 break 语句结束循环。运行器将循环直到 Claude 返回一条不包含工具使用的消息。
如果你不需要中间消息,可以直接获取最终消息:
高级用法
在循环中,你可以完全自定义工具运行器对 Messages API 的下一个请求。运行器会自动将工具结果附加到消息历史中,因此你不需要手动管理它们。你可以选择性地检查工具结果以进行日志记录或调试,并在下一次 API 调用之前修改请求参数。
调试工具执行
当工具抛出异常时,工具运行器会捕获它并将错误作为带有 is_error: true 的工具结果返回给 Claude。默认情况下,只包含异常消息,不包含完整的堆栈跟踪。
要查看完整的堆栈跟踪和调试信息,请设置 ANTHROPIC_LOG 环境变量:
# View info-level logs including tool errors
export ANTHROPIC_LOG=info
# View debug-level logs for more verbose output
export ANTHROPIC_LOG=debug启用后,SDK 会记录完整的异常详情(使用 Python 的 logging 模块、TypeScript 中的 console 或 Ruby 的 logger),包括工具失败时的完整堆栈跟踪。
拦截工具错误
默认情况下,工具错误会传递回 Claude,然后 Claude 可以做出适当的响应。但是,你可能希望检测错误并以不同方式处理它们——例如,提前停止执行或实现自定义错误处理。
使用工具响应方法拦截工具结果,并在发送给 Claude 之前检查错误:
修改工具结果
你可以在工具结果发送回 Claude 之前修改它们。这对于添加元数据(如 cache_control)以启用工具结果的提示缓存,或转换工具输出非常有用。
使用工具响应方法获取工具结果,修改它,然后将修改后的版本添加到消息中:
当工具返回大量数据(如文档搜索结果)且你希望为后续 API 调用缓存这些数据时,向工具结果添加 cache_control 特别有用。有关缓存策略的更多详情,请参阅提示缓存。
流式传输
启用流式传输以在事件到达时接收它们。每次迭代产生一个流对象,你可以迭代它以获取事件。
SDK 工具运行器处于 beta 阶段。本文档的其余部分涵盖手动工具实现。
控制 Claude 的输出
强制工具使用
在某些情况下,您可能希望 Claude 使用特定工具来回答用户的问题,即使 Claude 认为它可以在不使用工具的情况下提供答案。您可以通过在 tool_choice 字段中指定工具来实现这一点,如下所示:
tool_choice = {"type": "tool", "name": "get_weather"}使用 tool_choice 参数时,我们有四个可选项:
auto允许 Claude 决定是否调用任何提供的工具。这是提供tools时的默认值。any告诉 Claude 它必须使用提供的工具之一,但不强制使用特定工具。tool允许我们强制 Claude 始终使用特定工具。none阻止 Claude 使用任何工具。这是未提供tools时的默认值。
使用提示缓存时,更改 tool_choice 参数将使缓存的消息块失效。工具定义和系统提示保持缓存,但消息内容必须重新处理。
下图说明了每个选项的工作方式:
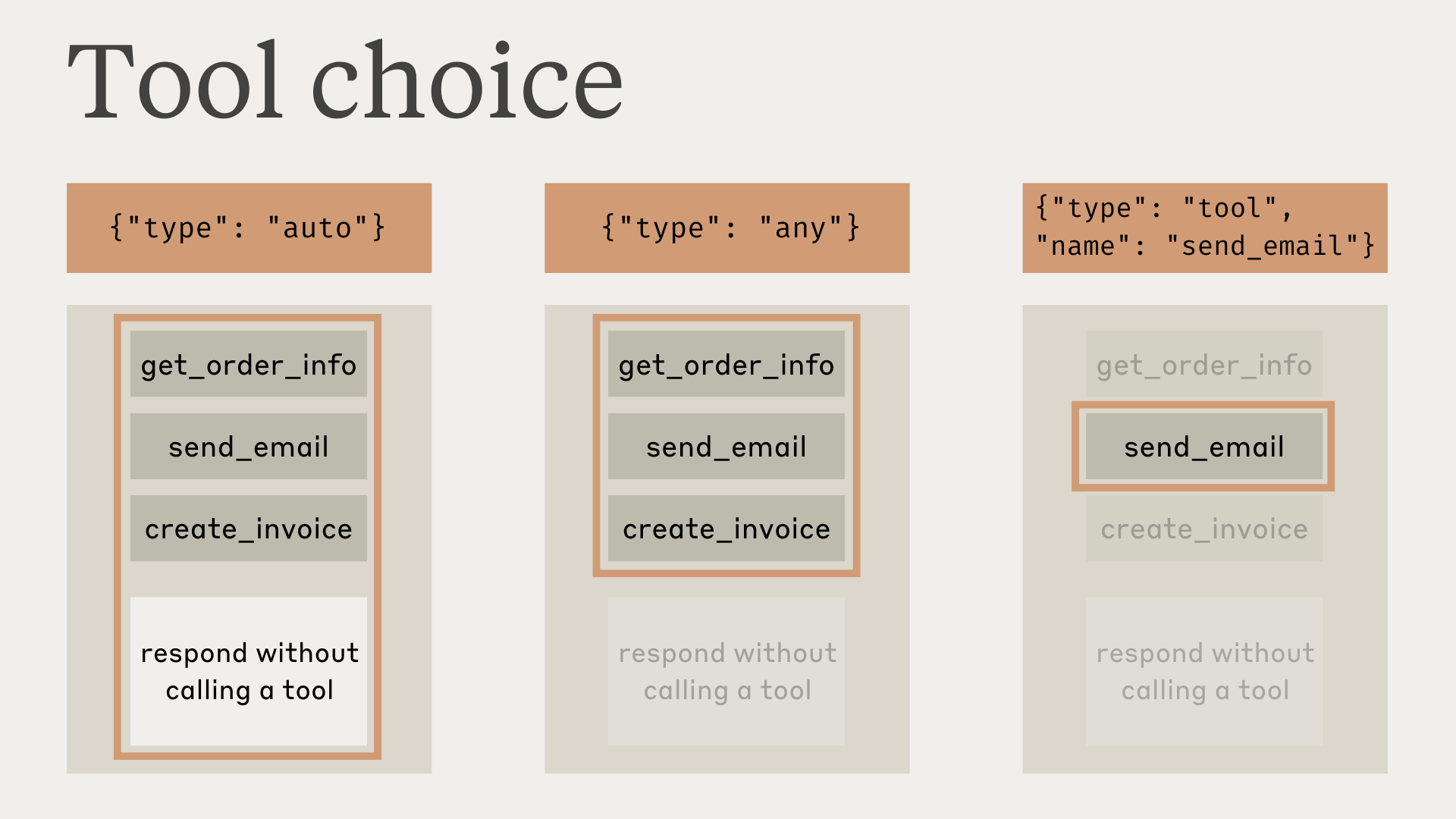
请注意,当您将 tool_choice 设置为 any 或 tool 时,我们将预填充助手消息以强制使用工具。这意味着模型不会在 tool_use 内容块之前发出自然语言响应或解释,即使被明确要求这样做。
将扩展思考与工具使用结合时,不支持 tool_choice: {"type": "any"} 和 tool_choice: {"type": "tool", "name": "..."},这将导致错误。只有 tool_choice: {"type": "auto"}(默认值)和 tool_choice: {"type": "none"} 与扩展思考兼容。
我们的测试表明这不会降低性能。如果您希望模型在仍然请求模型使用特定工具的同时提供自然语言上下文或解释,您可以将 tool_choice 设置为 {"type": "auto"}(默认值),并在 user 消息中添加明确的指令。例如:What's the weather like in London? Use the get_weather tool in your response.
使用严格工具保证工具调用
将 tool_choice: {"type": "any"} 与严格工具使用结合使用,以保证您的工具之一将被调用,并且工具输入严格遵循您的模式。在工具定义上设置 strict: true 以启用模式验证。
JSON 输出
工具不一定需要是客户端函数——您可以在任何需要模型返回遵循提供模式的 JSON 输出时使用工具。例如,您可以使用具有特定模式的 record_summary 工具。请参阅使用 Claude 的工具获取完整的工作示例。
使用工具时的模型响应
使用工具时,Claude 通常会在调用工具之前评论它正在做什么或自然地回应用户。
例如,给定提示"旧金山现在的天气怎么样,那里现在几点?",Claude 可能会这样回应:
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "I'll help you check the current weather and time in San Francisco."
},
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "toolu_01A09q90qw90lq917835lq9",
"name": "get_weather",
"input": {"location": "San Francisco, CA"}
}
]
}这种自然的响应风格帮助用户理解 Claude 正在做什么,并创造更具对话性的交互。您可以通过系统提示和在提示中提供 <examples> 来引导这些响应的风格和内容。
需要注意的是,Claude 在解释其操作时可能会使用各种措辞和方法。您的代码应该像处理任何其他助手生成的文本一样处理这些响应,而不依赖于特定的格式约定。
并行工具使用
默认情况下,Claude 可能会使用多个工具来回答用户查询。您可以通过以下方式禁用此行为:
- 当 tool_choice 类型为
auto时设置disable_parallel_tool_use=true,这确保 Claude 最多使用一个工具 - 当 tool_choice 类型为
any或tool时设置disable_parallel_tool_use=true,这确保 Claude 恰好使用一个工具
最大化并行工具使用
虽然 Claude 4 模型默认具有出色的并行工具使用能力,但您可以通过有针对性的提示来增加所有模型并行工具执行的可能性:
Claude Sonnet 3.7 的并行工具使用
Claude Sonnet 3.7 在响应中进行并行工具调用的可能性可能较低,即使您没有设置 disable_parallel_tool_use。我们建议升级到 Claude 4 模型,它们具有内置的 token 高效工具使用和改进的并行工具调用。
如果您仍在使用 Claude Sonnet 3.7,您可以启用 token-efficient-tools-2025-02-19 beta 头,这有助于鼓励 Claude 使用并行工具。您还可以引入一个"批量工具",作为元工具来同时包装对其他工具的调用。
请参阅我们 cookbook 中的此示例了解如何使用此解决方法。
处理工具使用和工具结果内容块
使用 Tool runner 更简单:本节描述的手动工具处理由 tool runner 自动管理。当您需要对工具执行进行自定义控制时,请使用本节内容。
Claude 的响应根据它使用的是客户端工具还是服务器工具而有所不同。
处理客户端工具的结果
响应将具有 tool_use 的 stop_reason 和一个或多个 tool_use 内容块,其中包括:
id:此特定工具使用块的唯一标识符。这将用于稍后匹配工具结果。name:正在使用的工具的名称。input:包含传递给工具的输入的对象,符合工具的input_schema。
当您收到客户端工具的工具使用响应时,您应该:
- 从
tool_use块中提取name、id和input。 - 在您的代码库中运行与该工具名称对应的实际工具,传入工具
input。 - 通过发送一条
role为user的新消息来继续对话,其中包含tool_result类型的content块和以下信息:tool_use_id:这是此结果对应的工具使用请求的id。content:工具的结果,可以是字符串(例如"content": "15 degrees")、嵌套内容块列表(例如"content": [{"type": "text", "text": "15 degrees"}])或文档块列表(例如"content": ["type": "document", "source": {"type": "text", "media_type": "text/plain", "data": "15 degrees"}])。这些内容块可以使用text、image或document类型。is_error(可选):如果工具执行导致错误,则设置为true。
重要的格式要求:
- 工具结果块必须紧跟在消息历史中对应的工具使用块之后。您不能在助手的工具使用消息和用户的工具结果消息之间包含任何消息。
- 在包含工具结果的用户消息中,tool_result 块必须在内容数组中排在最前面。任何文本必须在所有工具结果之后。
例如,这将导致 400 错误:
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Here are the results:"}, // ❌ 文本在 tool_result 之前
{"type": "tool_result", "tool_use_id": "toolu_01", ...}
]}这是正确的:
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "tool_result", "tool_use_id": "toolu_01", ...},
{"type": "text", "text": "What should I do next?"} // ✅ 文本在 tool_result 之后
]}如果您收到类似"tool_use ids were found without tool_result blocks immediately after"的错误,请检查您的工具结果格式是否正确。
收到工具结果后,Claude 将使用该信息继续生成对原始用户提示的响应。
处理服务器工具的结果
Claude 在内部执行工具并将结果直接纳入其响应中,无需额外的用户交互。
与其他 API 的区别
与将工具使用分离或使用特殊角色(如 tool 或 function)的 API 不同,Claude API 将工具直接集成到 user 和 assistant 消息结构中。
消息包含 text、image、tool_use 和 tool_result 块的数组。user 消息包含客户端内容和 tool_result,而 assistant 消息包含 AI 生成的内容和 tool_use。
处理 max_tokens 停止原因
max_tokens 停止原因如果 Claude 的响应因达到 max_tokens 限制而被截断,并且截断的响应包含不完整的工具使用块,您需要使用更高的 max_tokens 值重试请求以获取完整的工具使用。
# Check if response was truncated during tool use
if response.stop_reason == "max_tokens":
# Check if the last content block is an incomplete tool_use
last_block = response.content[-1]
if last_block.type == "tool_use":
# Send the request with higher max_tokens
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-opus-4-6",
max_tokens=4096, # Increased limit
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)处理 pause_turn 停止原因
pause_turn 停止原因使用 Web 搜索等服务器工具时,API 可能会返回 pause_turn 停止原因,表示 API 已暂停了一个长时间运行的回合。
以下是处理 pause_turn 停止原因的方法:
import anthropic
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
# Initial request with web search
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Search for comprehensive information about quantum computing breakthroughs in 2025"
}
],
tools=[{
"type": "web_search_20250305",
"name": "web_search",
"max_uses": 10
}]
)
# Check if the response has pause_turn stop reason
if response.stop_reason == "pause_turn":
# Continue the conversation with the paused content
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Search for comprehensive information about quantum computing breakthroughs in 2025"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response.content}
]
# Send the continuation request
continuation = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-7-sonnet-latest",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=messages,
tools=[{
"type": "web_search_20250305",
"name": "web_search",
"max_uses": 10
}]
)
print(continuation)
else:
print(response)处理 pause_turn 时:
- 继续对话:将暂停的响应原样传回后续请求中,让 Claude 继续其回合
- 根据需要修改:如果您想中断或重定向对话,可以选择在继续之前修改内容
- 保留工具状态:在继续请求中包含相同的工具以保持功能
错误排查
内置错误处理:Tool runner 为大多数常见场景提供自动错误处理。本节涵盖高级用例的手动错误处理。
在使用 Claude 的工具时,可能会出现几种不同类型的错误:
Was this page helpful?